Water crisis in Bengaluru is unprecedented
Many homes haven't installed RWH apparatus
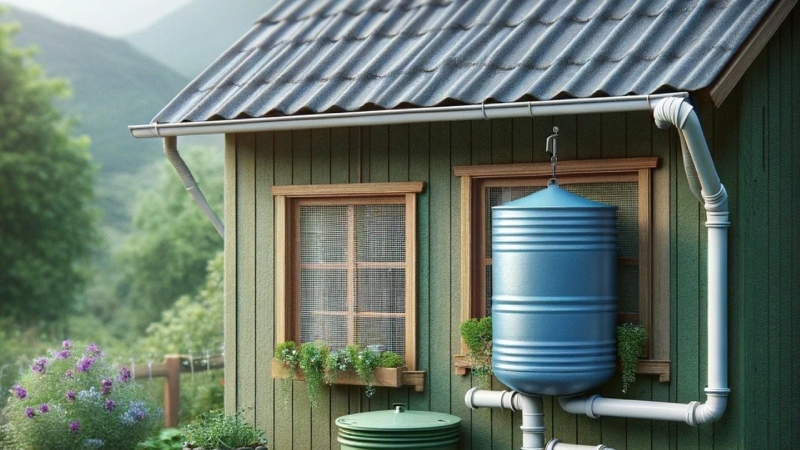
RWH is collection of rain water & using it for non-potable purposes
Bengaluru is facing an unprecedented water crisis. People are running from pillar to post to get water. With the onset of summer, it is speculated that things are only getting worse.
Now, the Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board (BWSSB) is of the opinion that the consequences of the water crisis could have been mitigated if only many households in the city had incorporated Rain Water Harvesting (RWH).
As per reports, only 2 lakh out of 10.8 lakh homes have the RWH apparatus. Well, on its part, the body has imposed a fine of Rs 40,000 on those households that have not set up RWH.
What is Rain Water Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is a technique used to collect and store rainwater for various purposes such as irrigation, household use, and replenishing groundwater. It involves the capture and storage of rainwater from surfaces like rooftops, pavements, and other surfaces, which would otherwise run off and be lost.
In Bengaluru, where water scarcity is a pressing issue, rainwater harvesting plays a crucial role in improving water sustainability. By capturing rainwater and using it for non-potable purposes such as gardening, flushing toilets, and washing clothes, RWH reduces the burden on the city’s municipal water supply. This, in turn, helps conserve freshwater resources and reduces the strain on existing water infrastructure. Additionally, by recharging groundwater aquifers through infiltration, rainwater harvesting helps replenish underground water sources, contributing to long-term water security for the city. Overall, rainwater harvesting is a sustainable solution that helps mitigate water scarcity and enhances water sustainability in Bengaluru.

Water crisis in Bengaluru is unprecedented
Many homes haven't installed RWH apparatus
RWH is collection of rain water & using it for non-potable purposes
Bengaluru is facing an unprecedented water crisis. People are running from pillar to post to get water. With the onset of summer, it is speculated that things are only getting worse.
Now, the Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board (BWSSB) is of the opinion that the consequences of the water crisis could have been mitigated if only many households in the city had incorporated Rain Water Harvesting (RWH).
As per reports, only 2 lakh out of 10.8 lakh homes have the RWH apparatus. Well, on its part, the body has imposed a fine of Rs 40,000 on those households that have not set up RWH.
What is Rain Water Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is a technique used to collect and store rainwater for various purposes such as irrigation, household use, and replenishing groundwater. It involves the capture and storage of rainwater from surfaces like rooftops, pavements, and other surfaces, which would otherwise run off and be lost.
In Bengaluru, where water scarcity is a pressing issue, rainwater harvesting plays a crucial role in improving water sustainability. By capturing rainwater and using it for non-potable purposes such as gardening, flushing toilets, and washing clothes, RWH reduces the burden on the city’s municipal water supply. This, in turn, helps conserve freshwater resources and reduces the strain on existing water infrastructure. Additionally, by recharging groundwater aquifers through infiltration, rainwater harvesting helps replenish underground water sources, contributing to long-term water security for the city. Overall, rainwater harvesting is a sustainable solution that helps mitigate water scarcity and enhances water sustainability in Bengaluru.