38% of the Indian population identifies as vegetarian
Vegetarianism encompasses various dietary preferences
Vegetarianism unveils a path towards holistic health
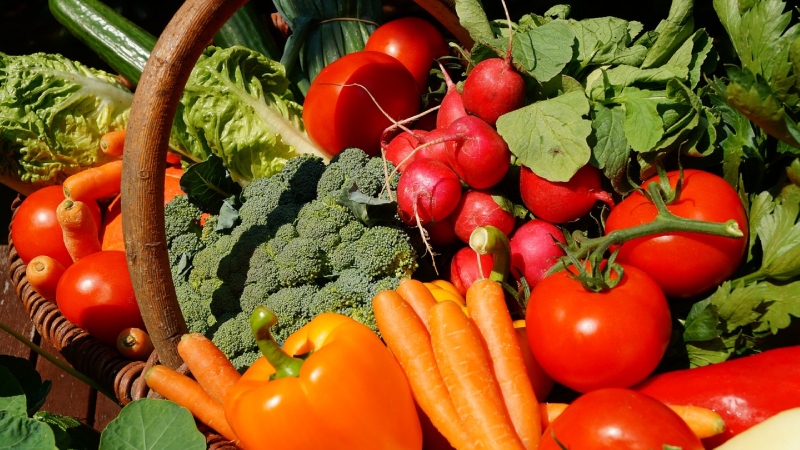
Vegetarianism has woven itself into the fabric of global culinary practices, with a burgeoning interest in plant-based diets for their sustainability and health benefits. India, where 38% of the population identifies as vegetarian, has long embraced this lifestyle. However, delving deeper reveals a diverse array of vegetarian diets beyond simply abstaining from meat and eggs.
The spectrum of vegetarianism encompasses various dietary preferences, each with its unique composition:
Also read: Mumbai: ‘Vegetarians only are allowed to sit here’ poster strokes controversy in IIT-Bombay
Benefits of vegetarianism extend beyond personal health to environmental sustainability and economic viability:
Moreover, protein adequacy in vegetarian diets can be achieved through combining complementary protein sources, such as grains with legumes or nuts with seeds, thus debunking the myth of protein deficiency.
As the world gravitates towards conscientious eating habits, understanding the nuances of vegetarianism unveils a path towards holistic health and environmental stewardship.

38% of the Indian population identifies as vegetarian
Vegetarianism encompasses various dietary preferences
Vegetarianism unveils a path towards holistic health
Vegetarianism has woven itself into the fabric of global culinary practices, with a burgeoning interest in plant-based diets for their sustainability and health benefits. India, where 38% of the population identifies as vegetarian, has long embraced this lifestyle. However, delving deeper reveals a diverse array of vegetarian diets beyond simply abstaining from meat and eggs.
The spectrum of vegetarianism encompasses various dietary preferences, each with its unique composition:
Also read: Mumbai: ‘Vegetarians only are allowed to sit here’ poster strokes controversy in IIT-Bombay
Benefits of vegetarianism extend beyond personal health to environmental sustainability and economic viability:
Moreover, protein adequacy in vegetarian diets can be achieved through combining complementary protein sources, such as grains with legumes or nuts with seeds, thus debunking the myth of protein deficiency.
As the world gravitates towards conscientious eating habits, understanding the nuances of vegetarianism unveils a path towards holistic health and environmental stewardship.